EBITDA per hectare is a financial metric used to measure the profitability of agricultural operations on a per-unit basis of land. EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It is a crucial indicator for farmers and agribusinesses as it reflects the efficiency and financial health of their farming activities without the influence of financing decisions, tax environments, and accounting practices.
Calculation of EBITDA per hectare
To calculate EBITDA per hectare, follow these steps:
- Determine Total EBITDA: Calculate the overall EBITDA by taking the total revenue generated from farming operations and subtracting the operating expenses, excluding interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Measure the Total Land Area: Measure the total hectares of land used for agricultural production.
- Compute EBITDA per Hectare: Divide the total EBITDA by the total number of hectares.
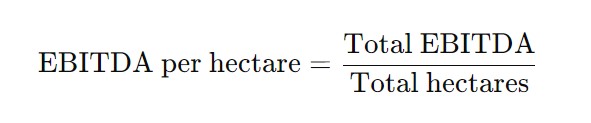
Importance in Agriculture
Using EBITDA per hectare helps in:
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing the profitability of different fields, crops, or farming practices on an equal basis.
- Investment Decisions: Making informed decisions on land purchases, leases, and the implementation of new agricultural technologies.
- Operational Efficiency: Identifying areas for cost reduction and operational improvements to enhance profitability.
Practical Example
A farm with a total EBITDA of $100,000 operating on 200 hectares of land would have an EBITDA per hectare of:

This metric can be used to assess the performance over different periods or compare with industry benchmarks.
Mandako Equipment and EBITDA
Efficient use of farming equipment significantly impacts EBITDA per hectare. Mandako’s range of agricultural machinery, such as their Land Rollers and Storm models, are designed to enhance soil preparation and crop management, thereby improving yield and reducing operating costs. By utilizing Mandako’s innovative equipment, farmers can potentially increase their EBITDA per hectare through better resource management and operational efficiency.

